<aside> 📘 TL;DR;
区块链的分布式账本有两个主流实现方式:账户模式(account model)和 UTXO model。
Ethereum 和传统金融(如银行)都采用账户模式,也就是在持久化的数据中,存储账户和余额。这样做的优点是更简单,但是要追踪每一笔钱的去向就变得比较困难。
BTC 采用的是 Unspent Transaction Outputs(UTXOs)模式,每个地址下记录的是尚未消费的入账记录(UTXO),每一个 UTXO 都包含一个金额和其源自的交易(Transaction)。每一个交易都由若干个 inputs 和 outputs 组成,其中 inputs 就是付款方支付的 UTXOs,outputs 就是收款方收到的 UTXOs。每一笔交易都会销毁输入的 UTXOs 同时诞生一些新的输出的 UTXOs。通过回溯交易历史,每个 UTXO 最终可以追溯到其由矿工挖出时产生的 coinbase 交易(coinbase transaction)。
综上所述,实际上每个人账户中的每一笔 BTC 都不是完全同质化的,它们可以通过 coinbase 交易 ID 和输出编号(output number)进行唯一识别。正是利用这一点,构建了 BRC-20/BRC-100/BRC-420 等 FT(代币)/NFT(非同质化代币)/铭文生态。
BTC 的每一笔交易的转账费用也通过其中所包含的 UTXO 数量来确定。因此,作为私人钱包管理者,应该尽量避免持有大量小额 UTXO。在网络转账费较低的时候,可以通过将小额 UTXO 批量转账给自己的方式,以较低成本汇聚成较大额的 UTXO。如果一个 UTXO 的面额小于转账费用,那么这个 UTXO 实际上已经失去了价值,被称为比特币尘埃(bitcoin dust)。
</aside>
<aside> 📘 Relates
Bitcoin’s UTXO Model: What Is It and How to Manage UTXOs | River
What Is the Lightning Network?
</aside>
While regularly buying bitcoin and securing it in self-custody is smart, most people do it incorrectly because they do not consider future expenses. If you frequently receive small amounts of bitcoin, you may be shocked by the high transaction fees you will pay when spending your bitcoin at some point in the future.
In this article, we explain how to reduce your future bitcoin transaction fees by managing Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs), an increasingly important consideration in a world where on-chain fees continue to rise. If you already understand UTXOs, feel free to jump ahead to “What is Bitcoin UTXO Management.”
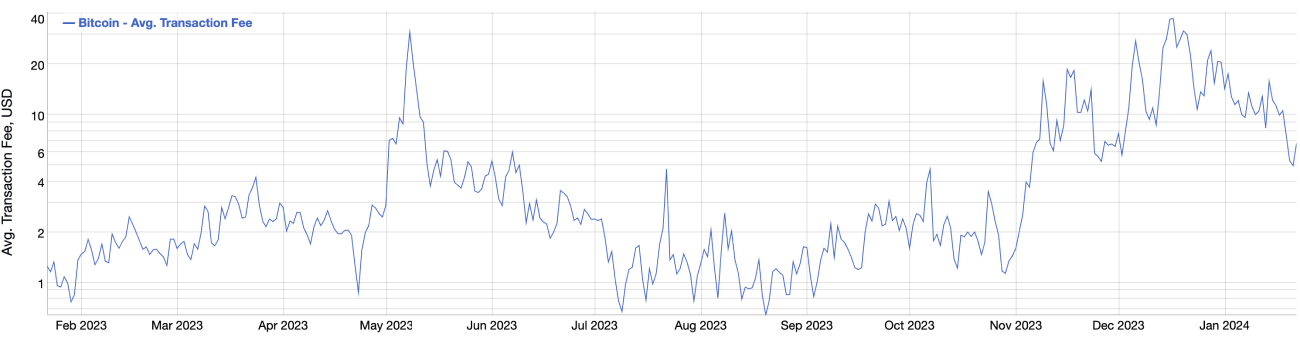
Here is a graph from bitinfocharts.com that illustrates the rising fees into 2024.

average bitcoin transaction fees in 2024
If you already understand UTXOs, feel free to jump ahead to “What is Bitcoin UTXO Management” or watch the video below:
https://youtu.be/_Qz_UlHgFAQ?si=sHlVu-ey-Dabt6g2
Unspent Transaction Outputs, or UTXOs, represent specific amounts of Bitcoin that you have received but not yet spent. Each UTXO is like an individual bill in your wallet, each with a unique value.
For example, a balance of 0.52 BTC in your wallet may consist of several UTXOs like 0.2, 0.15, and 0.17 BTC. Each UTXO is distinct and can hold any amount of bitcoin. They are the pieces of bitcoin you haven’t spent yet, and you use them to make new payments.
As its name suggests, a UTXO is an output of a bitcoin transaction. An output exists as a UTXO until it is used as an input in a future transaction. When someone sends you bitcoin, what you receive is a UTXO. The bitcoin balance in your wallet is the total of all the UTXOs received.
The UTXO set is the collection of all UTXOs on the bitcoin blockchain at any moment. Bitcoin nodes track this set to agree on identifying existing coins and their owners, helping to prevent the issue of double spending, which had plagued previous attempts at a decentralized digital currency.
➤ Learn more about The Double Spend Problem
UTXOs are created when existing ones are consumed by transactions. Each bitcoin transaction consists of inputs and outputs. Inputs in a transaction use up old UTXOs, while outputs generate new ones. So, if old UTXOs are destroyed to create new UTXOs, how are UTXOs created in the first place? Answer: coinbase transactions. This cycle starts with a coinbase transaction, which miners use to introduce new Bitcoin into the system, creating initial UTXOs without prior inputs.
A coinbase transaction is a special type of transaction that creates new bitcoin as a reward for the miner of a block. Since this transaction is creating new bitcoin, the coinbase transaction has no inputs and one or more outputs. Like all normal outputs, the output of a coinbase transaction is a new UTXO.
Each UTXO has the following characteristics: