<aside> 📘 Series:
该系列介绍了 Anonumous Credential(Anoncred)/Attribute-Based Credential(ABC)的概念,背后的算法原理 selective disclosure,具体的实现 CL signature、BBS+ signature。
Anonymous Credential Part 1: Brief Overview and History
Anonymous Credential Part 2: Selective Disclosure and CL Signature
Anonymous Credential Part 3: BBS+ Signature
</aside>
An anonymous credential (Anoncred), which is also known as an attribute-based credential (ABC), is a concept for a digital credential that provides a credential holder maximal privacy and an ability to selectively disclose their personal information.
“the user can later prove to a third party that she possesses a credential containing a given attribute or role without revealing any other information stored in the credential.”
— IBM Research

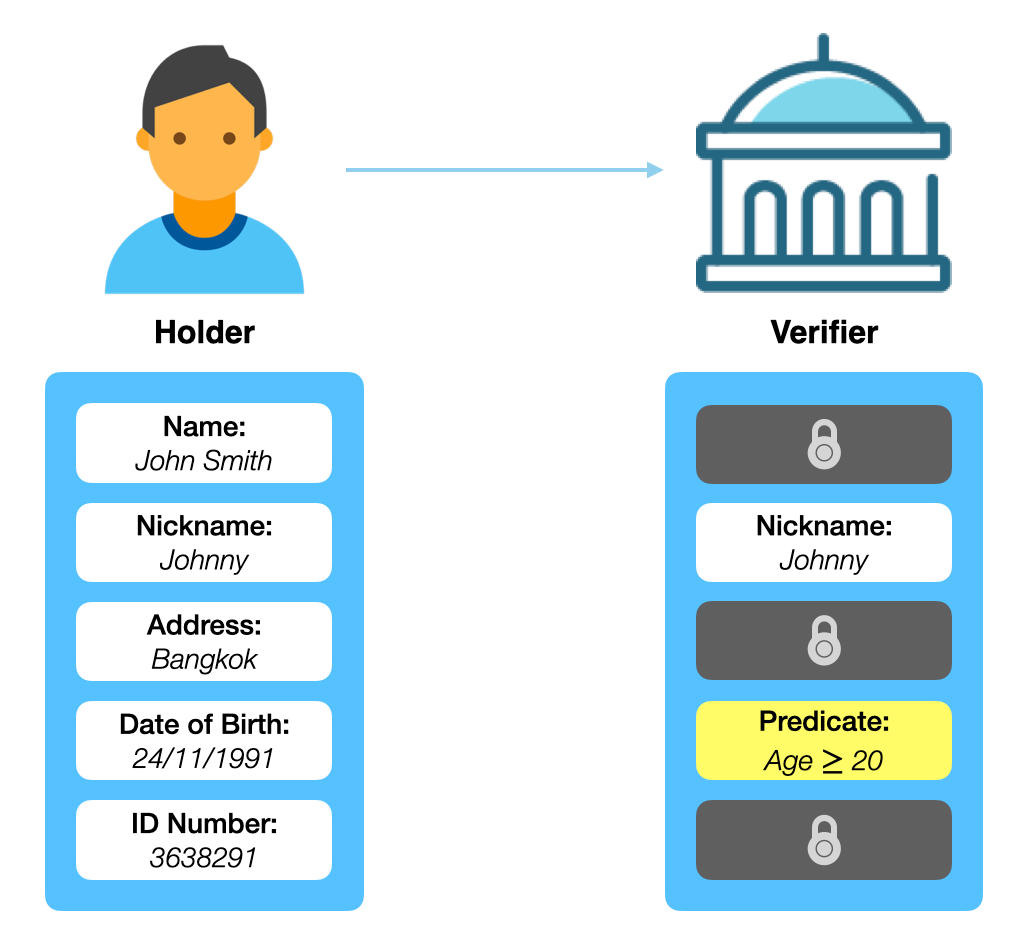
For example, a credential contains five attributes: name, nickname, address, date of birth and ID number. Using an Anoncred, the credential holder can choose to reveal and hide any of their attributes to a third party. A zero-knowledge proof could also be used with the Anoncred to, e.g., prove that their age is above 20 years old.
In recent years, an Anoncred is also considered as a verifiable credential containing a set of credential attributes, called claims. An Anoncred has the following properties.
Verifiable Credentials Data Model v1.1
Given the frequency of data breaches and the increasingly tightening data privacy regulations such as GDPR, the concept of Anoncreds is becoming more relevant than ever. In recent years, several big companies and startups have also started adopting Anoncreds, especially members of Decentralized Identity Foundation (DIF).
Here, we give a brief overview of theories for Anoncred and its application, of which we divide into four eras: